負の二項回帰モデルを R で行う方法
目次
負の二項モデルを R で行う方法
まず、データを読み込む
X <- c(rep(1, 913), rep(2, 1345), rep(3, 519), rep(9, 863))
Y <- c(rep(0, 910), rep(1, 2), rep(2, 1), rep(4, 0),
rep(0, 1333), rep(1, 11), rep(2, 1), rep(4, 0),
rep(0, 509), rep(1, 9), rep(2, 1), rep(4, 0),
rep(0, 849), rep(1, 13), rep(2, 0), rep(4, 1))
dat <- data.frame(X, Y)
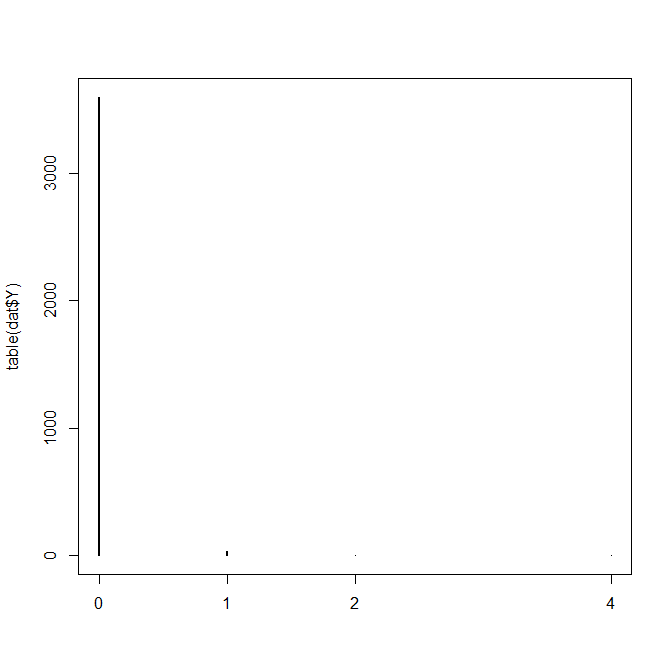
Yの分布を確認
> table(dat$Y)
0 1 2 4
3601 35 3 1
Yの分布図はすごいことに、なっている
plot(table(dat$Y))
XとYの関係を見ていこう
まずクロス集計表
> table(dat$X, dat$Y)
0 1 2 4
1 910 2 1 0
2 1333 11 1 0
3 509 9 1 0
9 849 13 0 1
Y がゼロばかりなのが目立つ
負の二項回帰モデルは、MASS パッケージの glm.nb() を使う
library(MASS)
nb.res <- glm.nb(Y ~ factor(X), data=dat)
summary(nb.res)
結果は、Xが1に比べて、3とか、9とかはYに関連がある
> summary(nb.res)
Call:
glm.nb(formula = Y ~ factor(X), data = dat, init.theta = 0.05009536409,
link = log)
Deviance Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-0.18802 -0.18228 -0.13295 -0.09165 3.10151
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) -5.4304 0.5214 -10.415 <2e-16 ***
factor(X)2 0.7912 0.6030 1.312 0.1895
factor(X)3 1.5764 0.6334 2.489 0.0128 *
factor(X)9 1.5032 0.5948 2.527 0.0115 *
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
(Dispersion parameter for Negative Binomial(0.0501) family taken to be 1)
Null deviance: 210.18 on 3639 degrees of freedom
Residual deviance: 199.65 on 3636 degrees of freedom
AIC: 465.67
Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 1
Theta: 0.0501
Std. Err.: 0.0236
2 x log-likelihood: -455.6660
まとめ
負の二項回帰モデルを R で実行する方法を簡単に紹介した
MASS パッケージの glm.nb() 関数を使うと実行できる




コメント